What is the alumino thermite process?
This reaction is driven by the strong affinity of aluminum for oxygen. Aluminum is highly reactive and readily combines with oxygen to form aluminum oxide. When aluminum is mixed with a metal oxide, it will react to steal the oxygen away from the metal, leaving the metal in its pure form. The heat generated by this reaction is so intense that it can melt the metal, making it ideal for welding and other industrial applications.
The process works because aluminum is a more reactive metal than iron, chromium, and other metals that are typically found in their oxide forms. This means that aluminum has a stronger desire to bond with oxygen than these other metals. When aluminum is mixed with an oxide of a less reactive metal, it will readily donate its electrons to the oxygen atoms in the oxide, effectively “stealing” them from the other metal. This transfer of electrons breaks the bond between the metal and oxygen in the oxide, releasing the metal in its pure form. The energy released in this process is significant, as it is the driving force behind the high temperatures observed in the alumino thermite reaction.
The alumino thermite process is commonly used in various industrial applications, including:
Welding: The intense heat generated by the reaction can be used to weld together metal components, especially those made of iron and steel.
Metal Production: This process can be used to extract pure metals from their oxides, such as the extraction of chromium from chromium oxide.
Demolition: The high temperatures generated can be used to cut through metal structures and demolish buildings.
The process is often employed in situations where conventional welding techniques are not practical, such as in remote locations where electricity is not readily available. It’s also used to create strong welds in situations where the metal components are too thick for conventional welding methods.
The alumino thermite process is a powerful and versatile chemical reaction that has a wide range of applications in various industries. Its ability to generate high temperatures and produce pure metals makes it an essential tool for welding, metal production, and demolition.
What is meant by thermite process?
Imagine you have a metal oxide, which is like a metal locked in a cage with oxygen. Aluminum acts as a key, breaking the bond between the metal and oxygen. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy, turning the metal into a liquid.
Think of it like this: You have a rusty metal object. Rust is essentially iron oxide. When you apply the thermite process, the aluminum reacts with the iron oxide, releasing heat and leaving behind molten iron. The heat generated in the reaction is so intense that it can melt the iron, creating a pool of liquid metal. This is the fundamental principle of the thermite process.
The thermite reaction is used in various applications, including welding, metal cutting, and even demolition. The intense heat generated in the reaction makes it ideal for these tasks. For instance, in welding, the molten metal produced by the thermite reaction is used to fuse two metal pieces together. This method is particularly useful for welding large structures, such as railway tracks.
The thermite reaction is a powerful tool in engineering and metallurgy, harnessing the exothermic nature of the reaction for various industrial applications.
What is the role of aluminium in the thermite process?
This reaction is driven by the fact that aluminum has a higher oxygen affinity than iron. This means aluminum has a stronger attraction to oxygen than iron does. When aluminum is mixed with iron(III) oxide, it readily combines with the oxygen, displacing the iron and forming aluminum oxide. The released iron is in a molten state, making the reaction extremely hot and useful for various applications like welding and cutting.
The thermite reaction releases a tremendous amount of energy, reaching temperatures of around 2,500°C (4,532°F), making it a highly exothermic reaction. This high temperature allows for the melting of the iron, which is why it’s used in thermite welding.
Here’s a breakdown of the reaction:
Aluminum (Al) + Iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃) → Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) + Iron (Fe)
It’s important to note:
* The thermite process is a highly reactive chemical reaction, so it needs to be handled with care.
* The reaction is self-sustaining, meaning it doesn’t need an external heat source to initiate once it starts.
* While the thermite reaction is used for welding, it also has other applications, such as in demolition, military munitions, and even for creating iron from its oxide ore.
The thermite reaction is a fascinating demonstration of the power of chemical reactions and the importance of oxygen affinity in determining the outcome of such reactions. Understanding this concept is crucial for appreciating the versatility of aluminum in various applications, particularly in the field of metallurgy.
What is alumino thermit welding process?
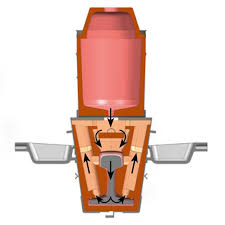
Let’s break down what’s happening. Aluminum is a very reactive metal. When it reacts with metal oxides like iron oxide (rust), it pulls the oxygen away from the metal. This process creates a lot of heat, melting both the metal and the aluminum. The molten metal then flows into a mold, where it solidifies, forming a strong weld.
This powerful reaction is what makes alumino-thermic welding so unique. The high temperatures allow for welding thick sections of metal, making it ideal for repairs and joining large structures. It’s also useful in situations where electricity is unavailable.
For example, if you’re repairing a broken railroad track, alumino-thermic welding can be used to quickly and efficiently join the two pieces back together. It’s also used in industries like shipbuilding and construction.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
1. The Ingredients: A mixture of aluminum powder and metal oxide is prepared, along with a small amount of ignition powder.
2. The Reaction: The ignition powder starts the reaction, which generates intense heat. The aluminum reduces the metal oxide, releasing molten metal.
3. The Weld: The molten metal is poured into a mold, where it solidifies, forming a strong weld.
Alumino-thermic welding is a fascinating process that leverages the power of chemistry to create strong and durable welds. It’s a valuable tool in various industries, and its versatility makes it a reliable choice for joining metals in diverse applications.
What is the importance of aluminothermic process?
One of the key reasons why the aluminothermic process is so important is its ability to produce high-purity metals like iron, manganese, chromium, and nickel. The intense heat generated by the reaction melts the metal, allowing impurities to be removed through slag formation. This high-purity metal is essential for various industries, particularly those demanding high-quality materials for construction, manufacturing, and technology.
Another advantage of the aluminothermic process is its effectiveness in welding and repairing large structures. This process is particularly suitable for welding railway tracks, repairing ship hulls, and joining massive steel structures. The intense heat generated by the reaction allows for a quick and efficient welding process, making it ideal for large-scale projects where conventional welding methods might be too time-consuming or impractical.
Furthermore, the aluminothermic process is also used in thermite welding and thermite cutting. This technique is used to cut and join thick metal pieces, especially in demolition and repairs. The process uses a mixture of iron oxide and aluminum powder to generate a molten iron pool, which effectively melts and cuts through the metal.
In summary, the aluminothermic process is a versatile and crucial technique with several important applications in various industries. Its ability to produce high-purity metals, weld and repair large structures, and perform thermite cutting and welding makes it a vital tool for modern engineering and construction projects.
Why is it called thermite reaction?
This reaction is called thermite because of the intense heat it produces. The word “thermite” comes from the Greek word “therme”, which means “heat.” So, the thermite reaction is basically a “heat-producing” reaction.
The thermite reaction is used for many things like welding, because the heat is so intense it can melt metal. Imagine having a portable furnace that you can use to weld railroad tracks together. That’s the power of thermite!
Here’s how it works: The aluminum reacts with the iron oxide (rust) to form aluminum oxide and liquid iron. This reaction releases so much energy that the iron melts, and it can get hot enough to reach temperatures over 2,500 degrees Celsius (4,532 degrees Fahrenheit) – that’s hot enough to melt steel!
So, the thermite reaction is named after the intense heat it produces, and it’s a fascinating example of how chemistry can be used to create incredible things.
What does aluminium act as in Aluminothermic process?
Let’s break down why aluminum is such a great reducing agent in the aluminothermic process. It all boils down to its chemistry. Aluminum is highly reactive, meaning it readily interacts with other substances. Its strong desire to lose electrons makes it a potent reducing agent.
When aluminum reacts with a metal oxide, like iron oxide (rust), it gives up its electrons to the iron ions in the oxide. This causes the iron ions to gain electrons and become neutral iron atoms. The aluminum, in turn, becomes oxidized, forming aluminum oxide. This reaction releases a significant amount of heat, making the process extremely exothermic.
The aluminothermic process is often used to extract metals from their oxides, particularly in situations where traditional smelting methods are not feasible. For example, it’s used to weld railroad tracks, repair broken machinery, and even produce certain alloys. The high temperatures generated by the reaction allow for the efficient melting and joining of metals, making it a valuable tool in various industries.
Which metal is extracted by Aluminothermic process?
The process relies on the high heat generated when aluminum reacts with metal oxides. When aluminum reacts with the oxide of the target metal, it releases a significant amount of heat, which is enough to melt the metal. This molten metal can then be collected and further processed.
Here’s a simplified explanation of the chemical reaction involved:
Metal Oxide + Aluminum → Metal + Aluminum Oxide + Heat
The aluminum oxide formed during the reaction is a stable compound and doesn’t readily react further. The process is commonly used in welding and also for the production of ferroalloys.
The Aluminothermic process is an efficient and cost-effective way to extract certain metals. It’s a testament to the power of chemical reactions and their ability to transform materials in surprising ways.
See more here: What Is Meant By Thermite Process? | What Is Meant By Alumino Thermite Process
See more new information: linksofstrathaven.com
What Is Meant By Alumino Thermite Process | What Is The Alumino Thermite Process?
Aluminothermic Reaction – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The Thermit process (see Example 5.5) involves the reaction of iron (III) oxide to provide the heat and molten iron needed for welding. Aluminum stands well above hydrogen in ScienceDirect
Reduction with aluminium (thermit process or alumino
The process is called thermic process or alumino-thermic process. EXAMPLES : (i) Manganese dioxide is reduced to manganese by heating with aluminium. 3MnO 2 + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al 2 O 3. (ii) Ferric oxide (Fe 2 Knowledge Base
What is aluminothermy and why it has to be done? – BYJU’S
Definition of Aluminothermy. : a process of producing great heat and strong chemical reduction by oxidizing finely divided aluminium with oxygen taken from another metal, BYJU’S
In alumino-thermite process, aluminium is used as – Toppr
Alumino thermite process involves reduction of chromium with oxide and aluminium. Toppr
What is Thermit Reaction? Explain its use and give
A thermite reaction is basically iron oxide (rust) reacting with aluminum to produce molten iron. The products are aluminium oxide, elemental iron, and a large amount of Toppr
Thermite Reaction: Definition, Formula, and Applications
A thermite reaction or process is an exothermic redox reaction between iron (III) oxide (Fe 2 O 3) and aluminum (Al) in powder form. This mixture of aluminum and iron oxide is chemistrylearner.com
Aluminothermic Process – Uses, Reaction, and,
The aluminothermic process has revolutionized how we produce metals such as iron and aluminum alloys because it provides an efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods while also ThePipingMart Blog
Thermite – Wikipedia
A thermite reaction, when used to purify the ores of some metals, is called the thermite process, or aluminothermic reaction. An adaptation of the reaction, used to obtain pure Wikipedia
Aluminothermic process | metallurgy | Britannica
Another thermochemical process is aluminothermic (thermite) joining. It has been successfully used for both ferrous and nonferrous metals but is more frequently used for britannica.com
Thermite Reaction Demo
Live Science: The Thermite Reaction
Aluminothermic Process
Alumino Thermite Process
Aluminothermy
Thermit Welding
Thermit Welding Used To Join Railway Tracks | Manufacturing Processes
Link to this article: what is meant by alumino thermite process.
See more articles in the same category here: https://linksofstrathaven.com/how
