Why is steam distillation better than simple distillation?
Think of it like this: imagine you’re trying to cook a delicate fish. You wouldn’t want to subject it to high heat for a long time, right? It would dry out and become tough. The same goes for delicate organic compounds. Steam distillation gently carries the compound away, preserving its integrity.
So, while vacuum distillation is another popular method, steam distillation shines when working with compounds that are easily damaged by heat. And the best part? The vapor produced during steam distillation is easily condensed, making it a clean and efficient process.
Why is steam distillation preferable to simple distillation?
Think of it like this: Imagine you’re trying to cook a delicate fish. You wouldn’t want to cook it at a high temperature, right? It would dry out and become tough. Steam distillation is like cooking the fish in a gentle steam bath, ensuring it stays moist and flavorful. The steam carries the volatile components of the plant material, like essential oils, away from the heat source, preventing them from being damaged. Simple distillation, on the other hand, is like throwing the fish directly into a hot pan – you might get it cooked, but it’s not going to be pretty (or tasty!).
This ability to work at lower temperatures is a key reason why steam distillation is often preferred for isolating heat-sensitive compounds found in plants, such as essential oils, fragrances, and other natural products.
Why is steam distillation preferred over regular distillation for isolating essential oils?
Think of it this way: Imagine you’re trying to cook a delicate dish. You wouldn’t want to use high heat, as it could burn the ingredients. Similarly, using high heat to extract essential oils could damage their chemical composition, altering their fragrance and therapeutic properties. Steam distillation provides a gentler approach, allowing us to extract these precious compounds without compromising their quality.
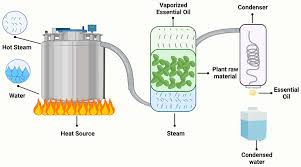
Here’s how it works: Steam is introduced into the plant material, and as the steam rises, it carries the VOCs with it. This steam mixture then passes through a condenser, where it cools down and condenses back into a liquid. This liquid contains the essential oil, which can then be separated from the water.
So, steam distillation is a win-win situation. Not only does it allow us to extract VOCs at a lower temperature, but it also prevents the degradation of these valuable compounds. It’s a method that truly respects the delicate nature of essential oils.
Why is steam distillation rather than simple distillation used to isolate eugenol What’s the difference?
What is the advantage of steam distillation?
Imagine you’re trying to extract a delicate floral scent from a plant. If you use regular distillation, the high temperatures could damage the scent molecules, making your final product weak or even ruined. Steam distillation, on the other hand, uses the power of steam to gently coax the scent molecules out of the plant material. The steam carries the scent molecules with it, and then the mixture is cooled down, allowing the scent molecules to separate and be collected.
This gentle approach to distillation is particularly useful for separating compounds like essential oils from plants. Essential oils are the concentrated aromatic compounds found in plants, and they’re often used in perfumes, aromatherapy, and even as natural remedies. Since many essential oils are sensitive to heat, steam distillation is the preferred method for extracting them, ensuring that the oils retain their unique fragrance and therapeutic properties.
What is the reason for embarking on steam distillation rather than simple distillation?
Let’s dive a little deeper into why steam distillation is the superior choice in this scenario:
Gentle Extraction: Steam distillation uses the power of steam to carry volatile compounds from the plant material. This gentle process prevents the compounds from being damaged by excessive heat, ensuring that they remain intact. Imagine it like this: the steam acts as a carrier, bringing the delicate compounds over at a lower temperature than they would normally boil at.
Preserving Quality: Many plant-based compounds, like essential oils, are heat-sensitive. Simple distillation, which involves boiling the material directly, can degrade these valuable compounds. Steam distillation avoids this issue by using the power of steam to extract them at a lower temperature.
Effective Separation: The steam carries the volatile compounds into the condenser where they cool down and condense. This process effectively separates the desired compounds from the plant material.
Versatility: Steam distillation is a versatile technique that can be used to extract a wide variety of compounds from various plant materials, including flowers, leaves, roots, and seeds.
In summary, steam distillation is a gentle, effective, and versatile method for extracting delicate compounds from plants. It allows us to capture the essence of these valuable compounds without sacrificing their quality.
What is the advantage of using steam distillation to isolate an organic liquid with a fairly high boiling point?
Think of it this way: Imagine you’re trying to cook a delicate dish that burns easily at high temperatures. You wouldn’t want to cook it on a super-hot stove, right? You’d use a lower heat setting to prevent burning. Similarly, steam distillation lets us “cook” our organic liquids at a lower temperature, preventing them from breaking down.
Here’s how it works:
Mixing with Steam: When you mix steam with the liquid, the steam carries the vaporized organic liquid into the distillation apparatus.
Reduced Pressure: Since the steam has a lower boiling point than the organic liquid, it helps lower the overall pressure within the system. This lower pressure further reduces the boiling point of the organic liquid.
Separation: The steam and the vaporized organic liquid are then condensed, separated, and collected.
Essentially, steam distillation allows us to distill high-boiling point organic liquids at a lower temperature, preserving their integrity and preventing decomposition. This is particularly useful for extracting essential oils and other delicate compounds from plants, where direct heating could damage the valuable molecules.
Let’s delve a bit deeper into why this is such a great advantage:
Minimizing Degradation: Imagine trying to boil a delicate flower to extract its fragrance. Direct heat could easily destroy the fragrant molecules. Steam distillation allows us to gently extract these compounds without causing them to break down.
Purity and Yield: Lowering the boiling point allows us to distill more effectively, resulting in a purer product with higher yields.
Versatility: Steam distillation is a versatile technique applicable to a wide range of compounds, from natural oils to pharmaceuticals.
So, next time you encounter a compound that’s sensitive to heat, remember that steam distillation might be the perfect solution to isolate it without compromising its integrity.
Which method of distillation is better?
Let’s delve deeper into how this process works. Imagine you have a mixture of two liquids with different boiling points. When you heat the mixture, the liquid with the lower boiling point will vaporize first. This vapor travels up the fractionating column and encounters the theoretical plates. As the vapor cools on these plates, it condenses back into liquid form. However, the condensed liquid is not pure. It contains some of the higher boiling point liquid too. But the vapor that rises from the condensed liquid is enriched with the lower boiling point component. As this process repeats on multiple plates, the vapor becomes increasingly enriched with the lower boiling point component. The vapor that finally reaches the top of the column is almost entirely the lower boiling point liquid. This separated liquid is then collected as the distillate.
In contrast, simple distillation uses a single round of evaporation and condensation. The vaporized liquid is collected without any further purification. This leads to less effective separation, especially when dealing with liquids that have boiling points close to each other.
Why is steam distillation better than simple distillation?
Imagine trying to boil a delicate flower. Using a simple distillation process, the high heat required would likely scorch the flower, destroying its delicate components. However, steam distillation allows you to gently extract the flower’s essence by introducing steam, which lowers the boiling point. This allows the flower’s fragrant oils to evaporate without being damaged by excessive heat.
Think of it this way: steam distillation acts like a gentle breeze, carrying away the volatile compounds without scorching them. Simple distillation can feel more like a harsh blast of heat, potentially ruining the compounds you’re trying to isolate.
This makes steam distillation an excellent choice for purifying organic compounds, particularly those that are sensitive to heat. While vacuum distillation is another effective method, steam distillation often proves to be a more efficient and gentler approach.
When is steam distillation used?
Think of it like this: Imagine you have a delicate flower that you want to extract its fragrance from. Heating the flower directly might ruin its scent. Steam distillation solves this problem by using steam to gently extract the fragrance without damaging the flower. The steam carries the volatile compounds, like essential oils, from the flower, and they condense back into a liquid mixture.
Let’s explore some examples:
Essential Oils: Steam distillation is widely used in the extraction of essential oils from plants. Many essential oils, such as rose oil and lavender oil, have boiling points higher than water. Direct heating would damage the delicate compounds responsible for their fragrance. Steam distillation gently extracts these oils without destroying them.
Fragrant Compounds: Similar to essential oils, steam distillation is a preferred method for extracting fragrant compounds from plants like jasmine and geranium. These compounds, often used in perfumes and aromatherapy, are sensitive to heat and can be easily damaged by direct heating. Steam distillation provides a safe and effective way to isolate these delicate fragrances.
Heat-Sensitive Materials: In the pharmaceutical industry, steam distillation is used for extracting delicate compounds from plants that are sensitive to high temperatures. This method ensures that the compounds are extracted without decomposition, preserving their medicinal properties.
In essence, steam distillation provides a gentle and effective way to extract valuable compounds from materials that are sensitive to high temperatures. It offers a safer alternative to direct heating, ensuring the preservation of the desired compounds and preventing unwanted reactions or decomposition.
How does simple distillation work?
The key to successful simple distillation is to ensure that the temperature of the boiling flask is maintained at a level where the vapor pressure of the desired component is significantly higher than the vapor pressure of any other components in the mixture. This is achieved by carefully controlling the heat input to the boiling flask. For example, if you are trying to separate water from ethanol, you would heat the mixture until the temperature reaches the boiling point of ethanol. At this point, the ethanol will vaporize and travel up the distillation column, while the water will remain in the boiling flask.
The efficiency of simple distillation is affected by the difference in boiling points of the components in the mixture. If the boiling points are very close together, the separation will be less efficient. This is because some of the lower-boiling component will vaporize along with the higher-boiling component, resulting in a less pure distillate.
One of the main advantages of simple distillation is that it is a relatively simple and inexpensive process. It is often used to separate liquids with significantly different boiling points, such as water and ethanol. However, simple distillation is not effective for separating liquids with boiling points that are close together, such as hexane and heptane.
In summary, simple distillation is a basic method used to separate liquids with different boiling points. It involves heating the mixture until the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes, then condensing the vapor and collecting the condensate in a separate container.
How does dry steam distillation work?
Here’s how it works:
1. Steam is generated: A boiler heats water to produce steam.
2. Steam is superheated: This steam is then heated even further, reaching a temperature higher than 100 degrees Celsius.
3. Steam flows through the plant material: The superheated steam is directed into a separate container holding the plant material.
4. Essential oils are extracted: As the superheated steam passes through the plant material, it breaks down the cell walls and releases the essential oils. The steam carries the essential oils with it.
5. Condensation: The steam mixture then moves to a condenser, where it cools down. This causes the steam to condense back into water, while the essential oils remain separate.
Why is superheated steam so important? It’s all about efficiency. The higher temperature of superheated steam allows it to penetrate the plant material more easily and extract the essential oils faster and more effectively. Think of it like this: if you were trying to melt a block of ice, you’d get better results with boiling water than with room temperature water.
Here’s a practical example: Let’s say you’re extracting essential oil from rosemary leaves. You want to ensure you extract as much of the oil as possible. By using superheated steam, you increase the heat transfer and allow the steam to penetrate the rosemary leaves more effectively. This leads to better extraction of the essential oils and a higher yield.
See more new information: linksofstrathaven.com
Steam Distillation: Why It’S Preferred For Isolation
Hey there, chemistry enthusiasts! Today we’re diving into the fascinating world of distillation techniques, specifically comparing steam distillation to simple distillation. You might be wondering why steam distillation is often the go-to method for isolating certain compounds. Let me break it down for you.
Imagine you’re trying to extract the delightful aroma of rose oil from delicate petals. Simple distillation, where you directly heat the petals, wouldn’t be the best approach. Why? Because the high temperatures required for boiling the petals could damage those precious oils, leaving you with a less-than-ideal result.
That’s where steam distillation comes to the rescue. It’s a gentler, more efficient method for isolating volatile compounds, like essential oils, from plant materials.
So, how does steam distillation work?
1. Steam Injection: We introduce steam into the mixture containing the compound we want to isolate. This steam carries heat energy and helps the compound vaporize.
2. Vapor Collection: The steam carrying the vaporized compound is then collected and condensed.
3. Separation: The condensed mixture is usually a two-phase system: the water phase and the organic phase containing the desired compound. These phases are easily separated.
Now, let’s delve into the advantages of steam distillation over simple distillation:
* Lower Boiling Point: Steam distillation allows us to isolate compounds at a lower temperature than their normal boiling point. This is because the compound vaporizes when mixed with steam, which has a lower boiling point than the compound itself. This gentleness prevents thermal degradation of sensitive compounds, preserving their quality.
* Reduced Thermal Degradation: Remember those delicate rose petals? Steam distillation prevents them from being directly exposed to high temperatures, protecting their valuable compounds from decomposition.
* Efficient for Non-Water-Soluble Compounds: Steam distillation is particularly effective for isolating compounds that are not soluble in water. The steam acts as a carrier, transporting the compound away from the source.
* Suitable for Heat-Sensitive Materials: For extracting compounds from materials that are sensitive to heat, steam distillation is a perfect choice. It’s like a gentle caress, not a harsh burning.
Let’s look at some real-world applications:
* Essential Oils: Steam distillation is the primary method for extracting essential oils from plants. Think lavender, peppermint, tea tree, and many more.
* Pharmaceuticals: This technique is used to isolate active compounds from medicinal plants, leading to the development of valuable pharmaceuticals.
* Flavor and Fragrance Industry: The fragrance industry relies heavily on steam distillation to extract fragrant compounds from flowers, spices, and other natural sources.
Let’s address some commonly asked questions:
1. What are the limitations of steam distillation?
While steam distillation is fantastic for isolating many compounds, it’s not a perfect solution for everything. There are some limitations:
* Not Suitable for High Boiling Point Compounds: For compounds with very high boiling points, steam distillation might not be effective. The steam wouldn’t be able to vaporize them efficiently.
* Potentially Long Process: Depending on the specific compound and the equipment used, steam distillation can sometimes be a relatively long process.
2. Can steam distillation be used for separating a mixture of compounds?
Yes, steam distillation can be used to separate mixtures of compounds, but only if the compounds have different volatilities. For instance, if you have a mixture of two compounds, one that vaporizes readily with steam and another that doesn’t, you can separate them using steam distillation. The compound with the higher volatility will be carried away by the steam, while the other will remain behind.
3. What are some other types of distillation?
Besides steam distillation and simple distillation, there are several other types of distillation techniques:
* Fractional Distillation: This is used to separate mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points. The process involves repeatedly vaporizing and condensing the mixture, gradually separating the components.
* Vacuum Distillation: This technique is used to distill compounds at lower temperatures than their normal boiling point. It’s particularly useful for isolating compounds that decompose at high temperatures.
4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of simple distillation?
Simple distillation is a straightforward technique, but it has some limitations compared to steam distillation:
Advantages:
* Simple and Inexpensive: Simple distillation is relatively easy to set up and doesn’t require specialized equipment.
* Effective for Separating Mixtures with Large Boiling Point Differences: If the components of a mixture have significantly different boiling points, simple distillation can be a viable option.
Disadvantages:
* Limited to Separating Mixtures with Significant Boiling Point Differences: Simple distillation is not effective for separating mixtures with similar boiling points.
* Potential for Thermal Degradation: High temperatures can damage heat-sensitive compounds during simple distillation.
Conclusion:
So, as you can see, steam distillation offers several advantages over simple distillation. It’s gentler, more efficient, and suitable for isolating volatile compounds from plant materials and other sources. However, remember that no single technique is perfect for every situation. Choose the distillation method that best suits your specific needs and the properties of the compound you want to isolate. Happy distilling!
5.5: Steam Distillation – Chemistry LibreTexts
Steam distillation is analogous to simple distillation, the main difference being that steam (or water) is used in the distilling flask along with the material to be distilled. Experimentally the Chemistry LibreTexts
Lab 7: Isolating Clove Oil from Cloves Using Steam Distillation
Why is steam distillation preferable to simple distillation for isolating high-boiling natural products? It is more preferable as it offers an advantage, volatile compounds Quizlet
Steam Distillation vs. Simple Distillation | Sciencing
Simple distillation normally brings a liquid to its boiling point, but when organic compounds are sensitive to heat, steam distillation is preferred. Sciencing
Steam Distillation – Principle, Advantages, How it
Steam distillation is a separation process which purifies isolate temperature-sensitive materials, such as natural aromatic compounds. Toppr
Isolation of Eugenol v2 – Westfield State University
Purpose. To perform a steam distillation using a microscale distillation apparatus and isolate a natural product from cloves. Background. The boiling point of eugenol, an oil Westfield State University
Steam distillation – Wikipedia
Simple distillation is generally done by boiling the starting material, because, once its vapor pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure, that still vapor-rich layer of air will be Wikipedia
Isolating Clove Oil from Cloves using Steam Distillation – Quizlet
Steam Distillation when one of the compounds is water. It offers an advantage in that volatile compounds that are unstable or have high boiling points can co-distill with water Quizlet
experimental chemistry – Different techniques of distillations …
Steam distillation take advantage of azeotropic effect, water steam is bubbled into your liquid (aromatic compound for example) and carry out the mixture of Chemistry Stack Exchange
Isolating Clove Oil from cloves using steam distillation – Quizlet
why steam distillation is preferable to simple distillation for isolating high-boiling natural products Quizlet
How Steam Distillation Works
Simple Distillation
Separating Liquids By Distillation
Steam Distillation
Steam Distillation And Extraction Of Eugenol From Cloves.
Gcse Chemistry – Fractional Distillation And Simple Distillation #50
An Introduction To Simple Distillation
Link to this article: why is steam distillation preferable to simple distillation for isolating.
See more articles in the same category here: https://linksofstrathaven.com/how