What are the 5 good conductors of heat?
Gold is a very good conductor of heat, but it’s also very expensive.
Silver is actually the best heat conductor among the metals, but it can be a bit pricey too.
Copper is a very efficient and affordable conductor, which is why it’s often used in cookware and pipes.
Aluminum is a lightweight and readily available conductor, making it popular for pots and pans.
Iron is a strong and durable conductor, but it isn’t as efficient as the others on this list.
But what makes these metals so good at transferring heat? It comes down to the way their atoms are arranged and how they interact with each other.
Metals have a special structure where their outer electrons are loosely bound to their atoms. These “free” electrons can move around easily, carrying energy with them. When heat is applied, these electrons get energized and start bouncing around, bumping into other atoms and transferring energy – that’s how heat flows through the metal.
Think of it like a game of hot potato, where the electrons pass energy along to each other. The more “free” electrons a metal has, and the more easily they can move, the better it will conduct heat. This is why silver, with its abundance of free electrons, is the champion of heat conductivity.
So next time you’re cooking up a storm or feeling the warmth of a sunny day, remember the amazing properties of metals that make these experiences possible!
Which element is the best conductor of electricity?
Let’s break it down a bit further. You know how atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons, right? Well, free electrons are electrons that are loosely bound to the atom and can easily move around. When you apply an electric field to silver, these free electrons start flowing, creating an electric current. The more free electrons a material has, the better it conducts electricity. That’s why silver is the champion!
Of course, silver isn’t the only good conductor. Copper is another excellent conductor and is actually more commonly used in electrical wiring because it’s cheaper. Gold is also a great conductor, but it’s even more expensive than silver, so it’s usually reserved for special applications like electronics.
Think of it like a crowded party. The more people there are, the easier it is to move around and get things done. The free electrons are like the people at the party, and the electric current is like the flow of people through the party. The more free electrons (people) you have, the easier it is for the electric current (people) to flow.
Which atoms are good conductors of heat and electricity?
Think of it like a sea of electrons constantly moving around within the metal. When heat is applied to one end of a metal object, these free electrons quickly absorb the energy and transfer it to other parts of the metal. This rapid transfer of energy is what makes metals such good conductors of heat.
Similarly, when an electric current is applied to a metal, these free electrons can easily carry the charge through the material. This is because they are not bound to any specific atom and can flow freely under the influence of an electric field.
Let’s break down how this happens:
The “Sea of Electrons”: Metals have a unique structure where their outer electrons are loosely bound to the atom. These electrons are not fixed to any particular atom and are free to move throughout the metal’s structure. This creates a “sea of electrons” that can easily flow and transfer energy.
Conducting Heat: When heat is applied to a metal, the free electrons absorb the energy and start moving faster. They collide with other atoms and electrons, transferring the heat energy throughout the material. This rapid transfer of energy is what makes metals excellent heat conductors.
Conducting Electricity: When an electrical potential is applied across a metal, the free electrons are attracted to the positive pole and repelled by the negative pole. They start flowing through the metal, creating an electric current. This free movement of electrons makes metals excellent electrical conductors.
So, the key takeaway is that the presence of these free electrons, readily available to move and carry energy, is what makes metals outstanding conductors of both heat and electricity.
Which elements are poor conductors of heat and electricity?
Non-metals are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity. This is because they have a different atomic structure than metals. Think of it this way: metals have a “sea” of freely moving electrons, which is why they conduct electricity so well. Non-metals, on the other hand, hold onto their electrons tightly, making it difficult for them to carry an electrical current. This same principle applies to heat as well.
Let’s take a look at an example: oxygen gas. Oxygen is a great example of a non-metal. It’s a gas at room temperature and doesn’t conduct electricity or heat very well. In fact, oxygen is often used as an insulator in electrical equipment to prevent electrical currents from flowing where they’re not supposed to.
Here’s a little more about why non-metals are poor conductors:
Atomic structure: Non-metals have a different atomic structure than metals. They tend to have more electrons in their outer shells, which makes them less likely to share or lose electrons. This means they don’t have the free-flowing electrons needed for good conductivity.
Bonding: Non-metals typically form covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons. These bonds are strong and don’t easily break, making it harder for electrons to move freely.
Melting point: Non-metals generally have lower melting points than metals. This is because the bonds between non-metal atoms are weaker than the bonds between metal atoms. Think about it this way: a solid non-metal can melt at a lower temperature because the atoms are not as tightly bound together.
Exceptions: There are some exceptions to this rule. For example, carbon can be a good conductor in some forms, like graphite. However, this is because the arrangement of carbon atoms in graphite creates a unique structure that allows for electron movement.
So, to sum it up: non-metals generally don’t conduct heat or electricity very well. This is due to their atomic structure, their bonding, and their lower melting points. Of course, there are some exceptions, but for the most part, non-metals are insulators!
What is a good conductor of heat and electricity?
Gold, silver, copper, and aluminum are excellent examples of materials that conduct heat and electricity well. This means they allow heat and electric current to flow through them easily. These materials are known as conductors.
But why are these materials so good at conducting? The answer lies in their atomic structure. Conductors have lots of free electrons, which are negatively charged particles that can move easily throughout the material. Think of it like a highway with lots of cars – the cars (electrons) can move freely and efficiently, allowing for the flow of heat and electricity.
On the other hand, insulators like paper, rubber, and plastics don’t have many free electrons. Their electrons are tightly bound to the atoms, making it difficult for them to move around. This means heat and electricity have a hard time flowing through them. Imagine it like a narrow, winding road with lots of traffic jams – it’s difficult for anything to move quickly and efficiently.
Now, let’s dive deeper into how the properties of conductors make them ideal for specific applications:
Gold: While it’s one of the best conductors, gold is often used in electronics because it’s corrosion-resistant. This means it doesn’t rust or tarnish easily, making it a reliable material for long-lasting electronic components. You’ll find gold used in things like connectors and integrated circuits.
Silver: Silver is actually the best conductor of heat and electricity. It’s even better than gold, but its cost makes it less practical for everyday use. However, silver is still used in specialized applications like high-performance electronics and solar panels.
Copper: Copper is a very good conductor and affordable, making it a popular choice for wiring and electrical components. Think about the wires in your home or the copper pipes in your plumbing – copper is everywhere!
Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight and also a good conductor, which is why it’s used in things like power lines and aircraft. It’s also used in many everyday items, like aluminum foil and beverage cans.
Understanding how conductors and insulators work is crucial in a wide range of fields, from engineering and technology to everyday life. The next time you see a wire or a circuit board, think about the amazing properties of these materials and how they contribute to the modern world!
What are the 5 best conductors of electricity?
Copper, gold, silver, steel, aluminum, and brass are among the best conductors of electricity. These metals are used in a wide variety of applications, from electrical wiring to computer chips. But why are they so good at conducting electricity?
It all boils down to the way their atoms are structured. Metals have a unique property: their electrons are loosely bound to their atoms, which allows them to move freely throughout the material. This is why metals are so good at conducting electricity. When you apply a voltage across a metal, the free electrons flow easily, creating an electric current.
Here’s a closer look at the top 5 best conductors of electricity:
1. Silver is the best conductor of electricity. It has a high conductivity and is resistant to corrosion. However, it’s also expensive, which limits its use in some applications.
2. Copper is a very good conductor of electricity and is also relatively inexpensive. This makes it a popular choice for electrical wiring and other applications.
3. Gold is another excellent conductor of electricity, but it’s even more expensive than silver. It’s often used in electronics where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in connectors and circuit boards.
4. Aluminum is a lightweight and inexpensive conductor of electricity. It’s widely used in electrical wiring, especially for long distances.
5. Steel is a good conductor of electricity, but it’s not as good as the other metals on this list. It’s often used in structural applications where its strength is more important than its conductivity.
So, when you think about the best conductors of electricity, remember these five top contenders. Each has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications.
What is the No 1 good conductor of electricity?
Silver’s high cost is why it’s rarely used for electrical applications. The cost is simply too high for most applications. For example, in everyday electrical wiring, copper is a more practical and cost-effective alternative. Copper is a good conductor and also much more affordable. It’s a great choice for everyday wiring.
When we talk about the best conductor, we need to consider more than just the material’s ability to conduct electricity. Practicality and cost are also important factors. That’s why copper is often the preferred choice for electrical wiring, despite being slightly less conductive than silver.
What is the best conductor of heat in all elements?
Silver is a phenomenal conductor of heat, even better than copper. It’s often used in applications where efficient heat transfer is crucial, like in electronics and specialized heat exchangers.
While steel and bronze are good conductors compared to other materials, they’re not as efficient as copper and aluminum.
You mentioned gold, iron, and other elements as good conductors of heat. This is accurate! Gold is actually a very good conductor of heat, though not as good as silver or copper. Iron is also a good conductor, but less efficient than the metals mentioned above.
Understanding the differences in thermal conductivity between metals helps us design and build things more efficiently!
Let’s break down the science behind why silver takes the crown for the best conductor of heat:
Free Electrons: Metals are made up of atoms arranged in a specific structure. These atoms have electrons that can move freely within the metal. These free electrons are the key to how well a metal conducts heat. When heat energy is applied to a metal, these free electrons absorb the energy and start moving faster. They then collide with other atoms and transfer the energy, which is how heat is conducted throughout the material.
The Structure of Silver:Silver has a unique atomic structure that allows its electrons to move exceptionally fast and easily. This structure, combined with the high density of free electrons, gives silver its remarkable thermal conductivity.
So, while copper is often the go-to choice for heat transfer in many applications, it’s important to remember that silver is the champion of heat conductivity. Its exceptional properties make it a valuable element in various technologies and industries.
What is the most conductive element?
But why is silver so good at conducting electricity? It all comes down to the way its atoms are arranged. Silver atoms have a single electron in their outermost shell, which is loosely bound to the atom. This means that these electrons can easily move around, and this movement is what allows electricity to flow.
Silver’s high conductivity makes it a valuable material in a variety of applications, including electronics, solar panels, and even jewelry. However, its high cost often makes it impractical for many applications. For example, copper is a cheaper and more readily available alternative, so it’s often used in wiring and other applications where cost is a major factor.
While silver might be the champion of conductivity, it’s not the only element that can conduct electricity. Many other metals, including copper, gold, and aluminum, are also excellent conductors. The key is to choose the right material for the job, taking into account factors such as cost, availability, and specific electrical requirements.
See more here: Which Element Is The Best Conductor Of Electricity? | Elements That Are Good Conductors Of Heat And Electricity Are
Which metals are good conductors of heat and electricity?
But how does this happen? Well, it all comes down to the way the atoms in metals are arranged. Metals have a special kind of bond called a metallic bond. In a metallic bond, the outer electrons of the metal atoms are loosely held. These electrons can move freely throughout the metal structure, like a sea of electrons.
Think of it like this: Imagine you have a bunch of marbles in a box. If you shake the box, the marbles will move around easily, bumping into each other. In a metal, these “marbles” are the free electrons. When heat or electricity is applied, these electrons can easily move and carry the energy with them. This is why metals are great conductors!
Now, let’s talk about some specific metals that are excellent conductors. Copper and aluminum are two of the best. They are widely used in electrical wiring and other applications where efficient heat or electricity transfer is essential. Silver is actually the best conductor of all metals, but it’s more expensive, so it’s not used as often. Gold is another good conductor, and it’s used in electronics because it doesn’t corrode easily.
So, the next time you see a piece of metal, remember that it’s full of tiny, free-moving electrons that are ready to carry heat or electricity!
Are metals good conductors?
Why? It all comes down to the way their atoms are structured. Metals typically have 1 to 3 electrons in their outermost shell. These electrons are loosely bound to the atom and can easily move around, making them free electrons. This is crucial for conductivity!
Silver and copper are considered the champions of conductivity. They excel at carrying both heat and electricity. On the other hand, lead isn’t as efficient at conducting heat, making it a poor conductor in this regard. Bismuth, mercury, and iron also fall short in the conductivity department.
Let’s delve a little deeper into the world of metallic conductivity.
Imagine a metal as a bustling city with a network of free-flowing electrons. These electrons are like tiny, energetic messengers constantly zipping around. When heat is applied to a metal, these electrons get even more energized, transferring the heat energy quickly throughout the city (the metal). This is why metals feel hot to the touch when heated. Similarly, when an electric current is applied, these electrons act like a highway, carrying the electrical charge from one point to another. That’s why metals are superb electrical conductors.
Think of it like this: the more free electrons a metal has, the better it conducts heat and electricity. That’s why metals like silver and copper, with their abundant free electrons, are the best in the conductivity game.
So, next time you reach for a metal spoon or wire, remember the hidden world of free electrons buzzing within, making it a fantastic conductor of heat and electricity.
Which metal is the poorest conductor of heat?
You might be surprised to learn that lead is actually a pretty poor conductor of heat. It’s not the worst, though! Bismuth, mercury, and iron are also not very good at conducting heat.
Let’s talk a bit more about why lead is a poor conductor. It’s all about how its atoms are arranged and how they interact. In metals that are good conductors, like copper or silver, the electrons move freely. They can carry heat energy easily from one part of the metal to another. But in lead, the electrons are more tightly bound to the atoms. This makes it harder for them to move around, and therefore harder for heat to travel through the material.
Think of it like this: imagine you have a big crowd of people trying to get through a narrow doorway. If everyone is pushing and shoving, it’s going to take a long time for them all to get through. That’s kind of what happens with the electrons in a poor conductor.
Let’s dive a bit deeper into this. The way the atoms are arranged in a metal, called its crystal structure, plays a big role in how well it conducts heat. Lead has a unique structure called a face-centered cubic lattice that makes it harder for heat to travel through it. In this structure, the atoms are packed very tightly together, which restricts the movement of electrons.
Also, the valence electrons – those that are involved in chemical bonding – in lead are more tightly bound to the atoms compared to other metals. This makes it harder for them to carry heat energy.
So, the next time you see a lead pipe, remember that it’s not just heavy; it’s also a pretty bad conductor of heat. Maybe it’s not the best choice for your next hot water plumbing project!
What is a good conductor of electricity?
What is a Good Conductor of Electricity?
Think of electricity like a bunch of tiny, energetic particles called electrons. These electrons are constantly moving around, and when they flow in a specific direction, that’s what we call electricity. Some materials let these electrons zip around easily, while others act like roadblocks.
Materials that allow electrons to flow easily are called conductors. Think of them as smooth highways for electricity. Silver is the best conductor, followed closely by copper and gold. These metals are excellent choices for wiring and electrical components because they let electricity flow efficiently.
But how do we know what makes a good conductor?
It’s all about the mobility of electrons. The more easily electrons can move through a material, the better the conductor.
Here’s why certain materials are better conductors than others:
Atomic Structure: In metals like silver, copper, and gold, the outermost electrons are loosely bound to the atoms. This means they can easily detach and move freely within the material. Imagine them like marbles rolling around in a bowl.
Temperature: Temperature plays a role too. As temperature increases, atoms vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move smoothly. So, conductors become less efficient at higher temperatures.
Let’s dive deeper into the properties of good conductors:
High Conductivity: This is the ability to conduct electricity easily. A good conductor has a low resistance to the flow of electrons, meaning the electrons encounter minimal obstacles.
Ductility: This means the material can be stretched into thin wires. This property makes metals like copper ideal for creating long, flexible wires used in electrical systems.
Malleability: This means the material can be hammered into thin sheets. This property is useful in applications like electrical contacts and other components.
By understanding these properties, you can see why silver, copper, and gold are considered the top contenders in the world of electricity. They’re like the superhighways of the electrical world, enabling the flow of energy that powers our modern lives.
See more new information: linksofstrathaven.com
Elements That Are Good Conductors Of Heat And Electricity Are: The Key To Technology
What Makes an Element a Good Conductor?
Think of conductivity like a highway for electrons. In simple terms, good conductors have electrons that are loosely bound to their atoms. These electrons are like little cars that can move freely, carrying energy like heat or electricity with them.
Metals: The Champions of Conductivity
When it comes to heat and electricity conduction, metals are the undisputed champions. They’re the stars of the show! Why? Because their atomic structure allows for easy electron movement.
Think of it like this: metals have a “sea” of free-moving electrons. These electrons are like the cars on our highway, ready to carry energy wherever it needs to go. This is why we use copper wires for electrical wiring, aluminum for cookware, and gold for electronics – these metals are excellent conductors!
Let’s break down some of the top metal conductors:
Silver: The undisputed champion! It’s the best conductor of both heat and electricity. That’s why it’s used in high-performance electronics and jewelry.
Copper: A close second to silver, copper is readily available and cost-effective, making it the go-to choice for electrical wiring and plumbing.
Gold: While not the best conductor, gold is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, making it ideal for use in electronics and jewelry.
Aluminum: A lightweight and affordable alternative to copper, aluminum is widely used for electrical wiring, foil, and cookware.
Beyond Metals: Other Good Conductors
While metals dominate the conductivity scene, there are other materials that can conduct heat and electricity to a lesser extent:
Carbon: In its pure form, carbon is a decent conductor of both heat and electricity. This is why it’s used in things like batteries, electrical contacts, and even some high-tech materials.
Graphite: A form of carbon, graphite is a good conductor of electricity. That’s why it’s used in pencils, lubricants, and even electrodes in batteries.
Water: Pure water is actually a poor conductor. However, the presence of dissolved impurities like salts makes it a much better conductor. This is why we should be careful around water when dealing with electricity!
Factors Affecting Conductivity
Several factors can influence how well an element conducts heat and electricity. Let’s explore a few key ones:
Temperature: Generally, as the temperature of a material increases, its conductivity decreases. This is because the atoms vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move freely.
Impurities: Even small amounts of impurities in a material can significantly reduce its conductivity. Think of those impurities as potholes on our highway, slowing down the flow of electrons.
Crystal Structure: The arrangement of atoms in a material can also influence conductivity. A regular, organized structure often leads to better conductivity compared to a disordered one.
Applications of Good Conductors
Now that we understand the basics of conductivity, let’s explore some practical applications in our daily lives:
Electrical Wiring: Copper and aluminum are the backbone of our electrical systems, conducting electricity from power plants to our homes and devices.
Electronics: Metals like gold, silver, and copper are essential in electronics, ensuring efficient signal transmission and heat dissipation.
Heating and Cooling: Copper and aluminum are used in heating and cooling systems to transfer heat efficiently, making our homes comfortable.
Cooking: Aluminum pots and pans conduct heat quickly and evenly, allowing us to cook delicious meals.
Understanding Conductivity: A Summary
To recap, good conductors are materials that allow heat and electricity to flow easily through them. Metals like silver, copper, gold, and aluminum are the top performers. They possess a “sea” of free-moving electrons that can readily carry energy. Other conductors like carbon and graphite also play important roles in various applications.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
A: A conductor allows heat and electricity to flow through it easily, while an insulator resists the flow of both. Think of an insulator like a wall that blocks the flow of energy. Examples of insulators include rubber, glass, and wood.
Q: How does temperature affect conductivity?
A: Generally, as temperature increases, conductivity decreases. This is because increased heat causes atoms to vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move freely.
Q: Why is gold used in electronics?
A: Gold is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, making it ideal for use in electronics where long-lasting performance is critical.
Q: What is the role of carbon in electrical conductivity?
A: Carbon, in its pure form, is a good conductor of electricity. It’s used in batteries, electrical contacts, and even some high-tech materials.
Q: How does impurities affect conductivity?
A: Impurities can significantly reduce conductivity. They act like obstacles, hindering the free flow of electrons.
Q: What are some examples of good conductors in everyday life?
A: Copper wiring, aluminum cookware, gold in electronics, and silver in jewelry are all examples of good conductors we encounter daily.
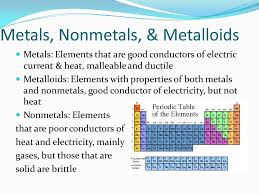
2.11: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids – Chemistry LibreTexts
All elements except hydrogen, which form positive ions by losing electrons during chemical reactions are called metals. Thus metals are electropositive elements. They are characterized by bright luster, hardness, ability to resonate sound and are excellent Chemistry LibreTexts
7.6: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids – Chemistry LibreTexts
Conduction: Metals are good conductors because they have free electrons. Silver and copper are the two best conductors of heat and electricity. Lead is the poorest Chemistry LibreTexts
Conductors – Good Conductor of Electricity, Types, Examples,
What is an electrical conductor? What makes a material a good conductor of electricity? Know the types of conductor, properties and good conductor of electricity with BYJU’S
6.5: Metals – Chemistry LibreTexts
A metal is an element that is a good conductor of heat and electricity. Metals are also malleable, which means that they can be hammered into very thin sheets Chemistry LibreTexts
Properties of metals – Metals – AQA Synergy – BBC
AQA Synergy. Metals – AQA Synergy Properties of metals. Metals have giant structures of atoms with delocalised electrons. This explains their high melting and boiling points and BBC
3.4: The Periodic Table | Introductory Chemistry – Lumen Learning
Learn how the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers and how they are organized in the periodic table. Find out which elements are metals, Lumen Learning
Metals and non-metals – Edexcel Metals vs non-metals – BBC
properties. of metals and non-metals. Some. elements. have properties that are not typical. For example: mercury (a metal) has a low. melting point. and exists as a liquid at room BBC
What is a Metal – UW Departments Web Server
Metals are opaque, lustrous elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity. Most metals are malleable and ductile and are, in general, denser than the other elemental UW Departments Web Server
Examples of Conductors and Insulators – Science Notes and
Materials that conduct electrons, protons, or ions are electrical conductors. They conduct electricity. Materials that conduct heat are thermal conductors. sciencenotes.org
Conductors And Insulators – Examples, Definition, Properties | Video For Kids
Which Metals Conduct Electricity The Best? | Metal Supermarkets
Heat Conductivity Metals
To Distinguish Between Good Conductors And Poor Conductors Of Heat
Conductors \U0026 Non-Conductors | Properties Of Matter | Chemistry | Fuseschool
Why Metals Are Good Conductors Of Heat ?
Conductors And Insulators || Science Educational Video For Kids
Link to this article: elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity are.
See more articles in the same category here: https://linksofstrathaven.com/how
